Energy Concepts
 | ||
| Energy Forms |
- Power:Physical strength and/or force being exerted on something.
- Unit:Unit it of measurement. ALWAYS LABEL YOUR UNITS.
- Conversions:The change from one unit, to another.
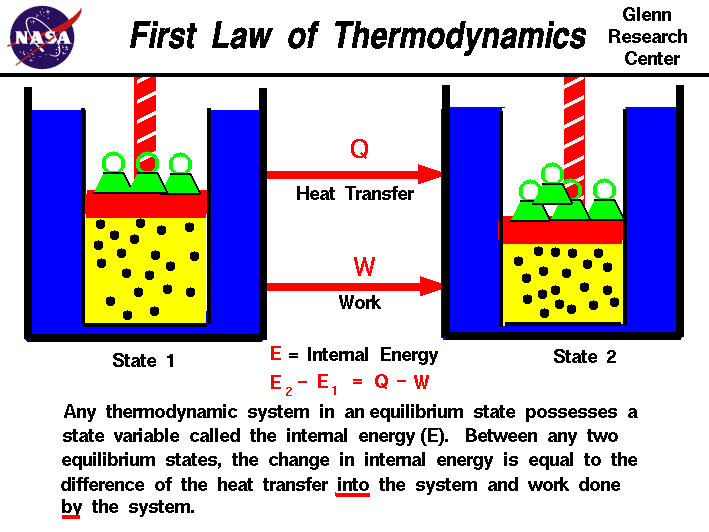 | |
| First Law of Thermodynamics |
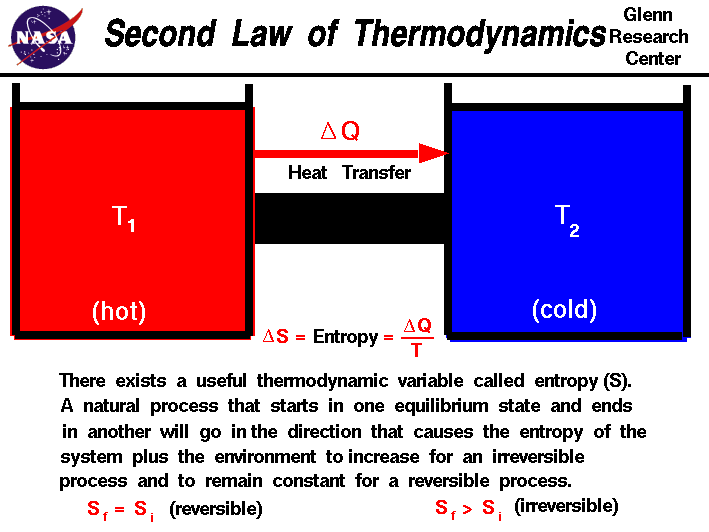 |
| Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy Consumption
 | ||
| Global Energy Use |
 |
| Future Energy Needs |
Fossil Fuel Resources and Use
- The formation fossil fuels(primarily natural gas, oil, and coal) came from dead organism matter millions of years ago. As soil sediment built up, oxygen was put out and the matter turned into kerogen, later turning into oil which puts off natural gas.
- Coal:Coal is mined, then workers put the surface back together and move on, leaving it ruined.
- Synfuels:Synthetic fuel made from coal or other sources as a substitute.
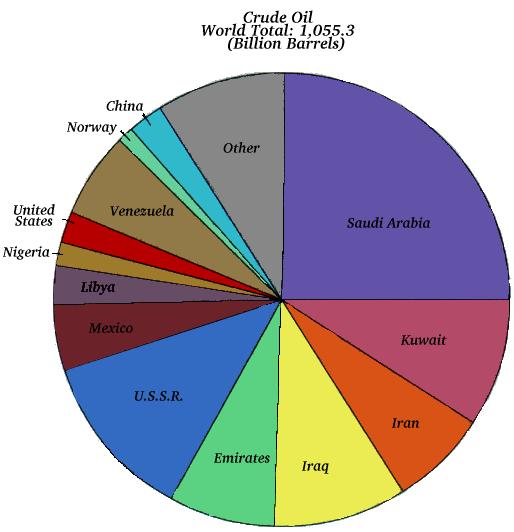 |
| World Reserves |
Nuclear Energy
 |
| Nuclear Fission Process |
- Hydroelectric power is the process of producing energy from moving water. Dams can help to produce hydroelectric power, as water passes through a dam, energy is created. The more water that passes through, the more energy that is produced. Dams can be helpful in producing power but they can also be harmful to animals. Dams also assist in flood control with producing hydroelectric power.
- Energy Efficiency:Systems that use less energy to do the same job as the conventional system.
- CAFE Standards:Regulations in the U.S. that are meant to improve the fuel economy.
- Mass Transit:Public transportation in an urban area.
Renewable Energy
 |
| Renewable Energy |
No comments:
Post a Comment